Table of Contents
- LibFile: lists.scad
- File Contents
- Section: List Query Operations
- Function: is_homogeneous()
- Function: min_length()
- Function: max_length()
- Function: list_shape()
- Function: in_list()
- Section: List Indexing
- Function: select()
- Function: slice()
- Function: last()
- Function: list_head()
- Function: list_tail()
- Function: bselect()
- Section: List Construction
- Section: List Modification
- Function: reverse()
- Function: list_rotate()
- Function: shuffle()
- Function: repeat_entries()
- Function: list_pad()
- Function: list_set()
- Function: list_insert()
- Function: list_remove()
- Function: list_remove_values()
- Section: List Iteration Index Helper
- Section: Lists of Subsets
- Section: Changing List Structure
- Section: Set Manipulation
This file contains Unicode characters that might be confused with other characters. If you think that this is intentional, you can safely ignore this warning. Use the Escape button to reveal them.
LibFile: lists.scad
Functions for operating on generic lists. Provides functiosn for indexing lists, changing list structure, and constructing lists by rearranging or modifying another list.
To use, add the following lines to the beginning of your file:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
Terminology:
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| List | An ordered collection of zero or more arbitrary items. ie: ["a", "b", "c"], or [3, "a", [4,5]] |
| Vector | A list of numbers. ie: [4, 5, 6] |
| Set | A list of unique items. |
File Contents
-
Section: List Query Operations
is_homogeneous()– Returns true if all members of a list are of the same type.min_length()– Given a list of sublists, returns the length of the shortest sublist.max_length()– Given a list of sublists, returns the length of the longest sublist.list_shape()– Returns the dimensions of an array.in_list()– Returns true if a value is in a list.
-
select()– Returns one or more items from a list, with wrapping.slice()– Returns part of a list without wrapping.last()– Returns the last item of a list.list_head()– Returns the elements at the beginning of a list.list_tail()– Returns the elements at the end of a list.bselect()– Select list items using boolean index list.
-
repeat()– Returns a list of repeated copies of a value.list_bset()– Returns a list where values are spread to locations indicated by a boolean index list.list()– Expands a range into a full list.force_list()– Coerces non-list values into a list.
-
reverse()– Reverses the elements of a list.list_rotate()– Rotates the ordering of a list.shuffle()– Randomizes the order of a list.repeat_entries()– Repeats list entries (as uniformly as possible) to make list of specified length.list_pad()– Extend list to specified length.list_set()– Sets the value of specific list items.list_insert()– Inserts values into the middle of a list.list_remove()– Removes items by index from a list.list_remove_values()– Removes items by value from a list.
-
Section: List Iteration Index Helper
idx()– Returns a range useful for iterating over a list.
-
pair()– Returns a list of overlapping consecutive pairs in a list.triplet()– Returns a list of overlapping consecutive triplets in a list.combinations()– Returns a list of all combinations of the list entries.permutations()– Returns a list of all permutations of the list entries.
-
Section: Changing List Structure
list_to_matrix()– Groups items in a list into sublists.flatten()– Flattens a list of sublists into a single list.full_flatten()– Recursively flattens nested sublists into a single list of non-list values.
-
set_union()– Merges two lists, returning a list of unique items.set_difference()– Returns a list of unique items that are in list A, but not in list B.set_intersection()– Returns a list of unique items that are in both given lists.
Section: List Query Operations
Function: is_homogeneous()
Alias: is_homogenous()
Synopsis: Returns true if all members of a list are of the same type.
Topics: List Handling, Type Checking
See Also: is_vector(), is_matrix()
Usage:
- bool = is_homogeneous(list, [depth]);
Description:
Returns true when the list has elements of same type up to the depth depth.
Booleans and numbers are not distinguinshed as of distinct types.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
the list to check |
depth |
the lowest level the check is done. Default: 10 |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = is_homogeneous([[1,["a"]], [2,["b"]]]); // Returns true
b = is_homogeneous([[1,["a"]], [2,[true]]]); // Returns false
c = is_homogeneous([[1,["a"]], [2,[true]]], 1); // Returns true
d = is_homogeneous([[1,["a"]], [2,[true]]], 2); // Returns false
e = is_homogeneous([[1,["a"]], [true,["b"]]]); // Returns true
Function: min_length()
Synopsis: Given a list of sublists, returns the length of the shortest sublist.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: max_length()
Usage:
- llen = min_length(list);
Description:
Returns the length of the shortest sublist in a list of lists.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
A list of lists. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
slen = min_length([[3,4,5],[6,7,8,9]]); // Returns: 3
Function: max_length()
Synopsis: Given a list of sublists, returns the length of the longest sublist.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: min_length()
Usage:
- llen = max_length(list);
Description:
Returns the length of the longest sublist in a list of lists.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
A list of lists. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
llen = max_length([[3,4,5],[6,7,8,9]]); // Returns: 4
Function: list_shape()
Synopsis: Returns the dimensions of an array.
Topics: Matrices, List Handling
See Also: is_homogeneous()
Usage:
- dims = list_shape(v, [depth]);
Description:
Returns the size of a multi-dimensional array, a list of the lengths at each depth.
If the returned value has dims[i] = j then it means the ith index ranges of j items.
The return dims[0] is equal to the length of v. Then dims[1] is equal to the
length of the lists in v, and in general, dims[i] is equal to the length of the items
nested to depth i in the list v. If the length of items at that depth is inconsistent, then
undef is returned. If no items exist at that depth then 0 is returned. Note that
for simple vectors or matrices it is faster to compute len(v) and len(v[0]).
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
v |
list to get shape of |
depth |
depth to compute the size of. If not given, returns a list of sizes at all depths. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = list_shape([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]]); // Returns [2,2,3]
b = list_shape([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]], 0); // Returns 2
c = list_shape([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]], 2); // Returns 3
d = list_shape([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[7,8,9]]]); // Returns [2,undef,3]
Function: in_list()
Synopsis: Returns true if a value is in a list.
Topics: List Handling
Usage:
- bool = in_list(val, list, [idx]);
Description:
Returns true if value val is in list list. When val==NAN the answer will be false for any list.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
val |
The simple value to search for. |
list |
The list to search. |
idx |
If given, searches the given columns for matches for val. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = in_list("bar", ["foo", "bar", "baz"]); // Returns true.
b = in_list("bee", ["foo", "bar", "baz"]); // Returns false.
c = in_list("bar", [[2,"foo"], [4,"bar"], [3,"baz"]], idx=1); // Returns true.
Section: List Indexing
Function: select()
Synopsis: Returns one or more items from a list, with wrapping.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: slice(), column(), last()
Usage:
- item = select(list, start);
- item = select(list, [s:d:e]);
- item = select(list, [i0,i1...,ik]);
- list = select(list, start, end);
Description:
Returns a portion of a list, wrapping around past the beginning, if end<start.
The first item is index 0. Negative indexes are counted back from the end.
The last item is -1. If only the start index is given, returns just the value
at that position when start is a number or the selected list of entries when start is
a list of indices or a range.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to get the portion of. |
start |
Either the index of the first item or an index range or a list of indices. |
end |
The index of the last item when start is a number. When start is a list or a range, end should not be given. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l = [3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
a = select(l, 5, 6); // Returns [8,9]
b = select(l, 5, 8); // Returns [8,9,3,4]
c = select(l, 5, 2); // Returns [8,9,3,4,5]
d = select(l, -3, -1); // Returns [7,8,9]
e = select(l, 3, 3); // Returns [6]
f = select(l, 4); // Returns 7
g = select(l, -2); // Returns 8
h = select(l, [1:3]); // Returns [4,5,6]
i = select(l, [3,1]); // Returns [6,4]
Function: slice()
Synopsis: Returns part of a list without wrapping.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: select(), column(), last()
Usage:
- list = slice(list, s, e);
Description:
Returns a slice of a list, from the first position s up to and including the last position e.
The first item in the list is at index 0. Negative indexes are counted back from the end, with
-1 referring to the last list item. If s is after e then the empty list is returned.
If an index is off the start/end of the list it will refer to the list start/end.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to get the slice of. |
start |
The index of the first item to return. Default: 0 |
end |
The index of the last item to return. Default: -1 (last item) |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = slice([3,4,5,6,7,8,9], 3, 5); // Returns [6,7,8]
b = slice([3,4,5,6,7,8,9], 2, -1); // Returns [5,6,7,8,9]
c = slice([3,4,5,6,7,8,9], 1, 1); // Returns [4]
d = slice([3,4,5,6,7,8,9], 5); // Returns [8,9]
e = slice([3,4,5,6,7,8,9], 2, -2); // Returns [5,6,7,8]
f = slice([3,4,5,6,7,8,9], 4, 3; // Returns []
g = slice([3,4,5], 1, 5; // Returns [4,5]
h = slice([3,4,5], 5, 7); // Returns []
Function: last()
Synopsis: Returns the last item of a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: select(), slice(), column()
Usage:
- item = last(list);
Description:
Returns the last element of a list, or undef if empty.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to get the last element of. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l = [3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
x = last(l); // Returns 9.
Function: list_head()
Synopsis: Returns the elements at the beginning of a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: select(), slice(), list_tail(), last()
Usage:
- list = list_head(list, [to]);
Description:
Returns the head of the given list, from the first item up until the to index, inclusive.
By default returns all but the last element of the list.
If the to index is negative, then the length of the list is added to it, such that
-1 is the last list item. -2 is the second from last. -3 is third from last, etc.
If the list is shorter than the given index, then the full list is returned.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to get the head of. |
to |
The last index to include. If negative, adds the list length to it. ie: -1 is the last list item. Default: -2 |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
hlist1 = list_head(["foo", "bar", "baz"]); // Returns: ["foo", "bar"]
hlist2 = list_head(["foo", "bar", "baz"], -3); // Returns: ["foo"]
hlist3 = list_head(["foo", "bar", "baz"], 1); // Returns: ["foo","bar"]
hlist4 = list_head(["foo", "bar", "baz"], -5); // Returns: []
hlist5 = list_head(["foo", "bar", "baz"], 5); // Returns: ["foo","bar","baz"]
Function: list_tail()
Synopsis: Returns the elements at the end of a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: select(), slice(), last()
Usage:
- list = list_tail(list, [from]);
Description:
Returns the tail of the given list, from the from index up until the end of the list, inclusive.
By default returns all but the first item.
If the from index is negative, then the length of the list is added to it, such that
-1 is the last list item. -2 is the second from last. -3 is third from last, etc.
If you want it to return the last three items of the list, use from=-3.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to get the tail of. |
from |
The first index to include. If negative, adds the list length to it. ie: -1 is the last list item. Default: 1. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
tlist1 = list_tail(["foo", "bar", "baz"]); // Returns: ["bar", "baz"]
tlist2 = list_tail(["foo", "bar", "baz"], -1); // Returns: ["baz"]
tlist3 = list_tail(["foo", "bar", "baz"], 2); // Returns: ["baz"]
tlist4 = list_tail(["foo", "bar", "baz"], -5); // Returns: ["foo","bar","baz"]
tlist5 = list_tail(["foo", "bar", "baz"], 5); // Returns: []
Function: bselect()
Synopsis: Select list items using boolean index list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: list_bset()
Usage:
- sublist = bselect(list, index);
Description:
Returns the items in list whose matching element in index evaluates as true.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
Initial list (or string) to extract items from. |
index |
List of values that will be evaluated as boolean, same length as list. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = bselect([3,4,5,6,7], [false,true,true,false,true]); // Returns: [4,5,7]
Section: List Construction
Function: repeat()
Synopsis: Returns a list of repeated copies of a value.
Topics: List Handling
Usage:
- list = repeat(val, n);
Description:
Generates a list of n copies of the given value val.
If the count n is given as a list of counts, then this creates a
multi-dimensional array, filled with val. If n is negative, returns the empty list.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
val |
The value to repeat to make the list or array. |
n |
The number of copies to make of val. Can be a list to make an array of copies. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = repeat(1, 4); // Returns [1,1,1,1]
b = repeat(8, [2,3]); // Returns [[8,8,8], [8,8,8]]
c = repeat(0, [2,2,3]); // Returns [[[0,0,0],[0,0,0]], [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]]
d = repeat([1,2,3],3); // Returns [[1,2,3], [1,2,3], [1,2,3]]
e = repeat(4, -1); // Returns []
Function: list_bset()
Synopsis: Returns a list where values are spread to locations indicated by a boolean index list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: bselect()
Usage:
- arr = list_bset(indexset, valuelist, [dflt]);
Description:
Opposite of bselect(). Returns a list the same length as indexlist, where each item will
either be 0 if the corresponding item in indexset is false, or the next sequential value
from valuelist if the item is true. The number of true values in indexset must be equal
to the length of valuelist.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
indexset |
A list of boolean values. |
valuelist |
The list of values to set into the returned list. |
dflt |
Default value to store when the indexset item is false. Default: 0 |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = list_bset([false,true,false,true,false], [3,4]); // Returns: [0,3,0,4,0]
b = list_bset([false,true,false,true,false], [3,4], dflt=1); // Returns: [1,3,1,4,1]
Function: list()
Synopsis: Expands a range into a full list.
Topics: List Handling, Type Conversion
See Also: scalar_vec3(), force_list()
Usage:
- list = list(l)
Description:
Expands a range into a full list. If given a list, returns it verbatim. If given a string, explodes it into a list of single letters.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
The value to expand. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l1 = list([3:2:9]); // Returns: [3,5,7,9]
l2 = list([3,4,5]); // Returns: [3,4,5]
l3 = list("Foo"); // Returns: ["F","o","o"]
l4 = list(23); // Returns: [23]
Function: force_list()
Synopsis: Coerces non-list values into a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: scalar_vec3()
Usage:
- list = force_list(value, [n], [fill]);
Description:
Coerces non-list values into a list. Makes it easy to treat a scalar input consistently as a singleton list, as well as list inputs.
- If
valueis a list, then that list is returned verbatim. - If
valueis not a list, andfillis not given, then a list ofncopies ofvaluewill be returned. - If
valueis not a list, andfillis given, then a listnitems long will be returned wherevaluewill be the first item, and the rest will contain the value offill.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
value |
The value or list to coerce into a list. |
n |
The number of items in the coerced list. Default: 1 |
fill |
The value to pad the coerced list with, after the firt value. Default: undef (pad with copies of value) |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
x = force_list([3,4,5]); // Returns: [3,4,5]
y = force_list(5); // Returns: [5]
z = force_list(7, n=3); // Returns: [7,7,7]
w = force_list(4, n=3, fill=1); // Returns: [4,1,1]
Section: List Modification
Function: reverse()
Synopsis: Reverses the elements of a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: select(), list_rotate()
Usage:
- rlist = reverse(list);
Description:
Reverses a list or string.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list or string to reverse. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
reverse([3,4,5,6]); // Returns [6,5,4,3]
Function: list_rotate()
Synopsis: Rotates the ordering of a list.
Topics: List Handling
Usage:
- rlist = list_rotate(list, [n]);
Description:
Rotates the contents of a list by n positions left, so that list[n] becomes the first entry of the list.
If n is negative, then the rotation is abs(n) positions to the right.
If list is a string, then a string is returned with the characters rotates within the string.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to rotate. |
n |
The number of positions to rotate by. If negative, rotated to the right. Positive rotates to the left. Default: 1 |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l1 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],-2); // Returns: [4,5,1,2,3]
l2 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],-1); // Returns: [5,1,2,3,4]
l3 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],0); // Returns: [1,2,3,4,5]
l4 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],1); // Returns: [2,3,4,5,1]
l5 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],2); // Returns: [3,4,5,1,2]
l6 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],3); // Returns: [4,5,1,2,3]
l7 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],4); // Returns: [5,1,2,3,4]
l8 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],5); // Returns: [1,2,3,4,5]
l9 = list_rotate([1,2,3,4,5],6); // Returns: [2,3,4,5,1]
Function: shuffle()
Synopsis: Randomizes the order of a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: sort(), sortidx(), unique(), unique_count()
Usage:
- shuffled = shuffle(list, [seed]);
Description:
Shuffles the input list into random order. If given a string, shuffles the characters within the string. If you give a numeric seed value then the permutation will be repeatable.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to shuffle. |
seed |
Optional random number seed for the shuffling. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
// Spades Hearts Diamonds Clubs
suits = ["\u2660", "\u2661", "\u2662", "\u2663"];
ranks = [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,"J","Q","K","A"];
cards = [for (suit=suits, rank=ranks) str(rank,suit)];
deck = shuffle(cards);
Function: repeat_entries()
Synopsis: Repeats list entries (as uniformly as possible) to make list of specified length.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: repeat()
Usage:
- newlist = repeat_entries(list, N, [exact]);
Description:
Takes a list as input and duplicates some of its entries to produce a list
with length N. If the requested N is not a multiple of the list length then
the entries will be duplicated as uniformly as possible. You can also set N to a vector,
in which case len(N) must equal len(list) and the output repeats the ith entry N[i] times.
In either case, the result will be a list of length N. The exact option requires
that the final length is exactly as requested. If you set it to false then the
algorithm will favor uniformity and the output list may have a different number of
entries due to rounding.
When applied to a path the output path is the same geometrical shape but has some vertices repeated. This can be useful when you need to align paths with a different number of points. (See also subdivide_path for a different way to do that.)
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
list whose entries will be repeated |
N |
scalar total number of points desired or vector requesting N[i] copies of vertex i. |
exact |
if true return exactly the requested number of points, possibly sacrificing uniformity. If false, return uniform points that may not match the number of points requested. Default: True |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
list = [0,1,2,3];
a = repeat_entries(list, 6); // Returns: [0,0,1,2,2,3]
b = repeat_entries(list, 6, exact=false); // Returns: [0,0,1,1,2,2,3,3]
c = repeat_entries(list, [1,1,2,1], exact=false); // Returns: [0,1,2,2,3]
Function: list_pad()
Synopsis: Extend list to specified length.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: force_list(), scalar_vec3()
Usage:
- newlist = list_pad(list, minlen, [fill]);
Description:
If the list list is shorter than minlen length, pad it to length with the value given in fill.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
A list. |
minlen |
The minimum length to pad the list to. |
fill |
The value to pad the list with. Default: undef |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
list = [3,4,5];
nlist = list_pad(list,5,23); // Returns: [3,4,5,23,23]
Function: list_set()
Synopsis: Sets the value of specific list items.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: list_insert(), list_remove(), list_remove_values()
Usage:
- list = list_set(list, indices, values, [dflt], [minlen]);
Description:
Takes the input list and returns a new list such that list[indices[i]] = values[i] for all of
the (index,value) pairs supplied and unchanged for other indices. If you supply indices that are
larger that the length of the list then the list is extended and filled in with the dflt value.
If you specify indices smaller than zero then they index from the end, with -1 being the last element.
Negative indexing does not wrap around: an error occurs if you give a value smaller than -len(list).
If you set minlen then the list is lengthed, if necessary, by padding with dflt to that length.
Repetitions in indices are not allowed. The lists indices and values must have the same length.
If indices is given as a scalar, then that index of the given list will be set to the scalar value of values.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
List to set items in. Default: [] |
indices |
List of indices into list to set. |
values |
List of values to set. |
dflt |
Default value to store in sparse skipped indices. |
minlen |
Minimum length to expand list to. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = list_set([2,3,4,5], 2, 21); // Returns: [2,3,21,5]
b = list_set([2,3,4,5], [1,3], [81,47]); // Returns: [2,81,4,47]
Function: list_insert()
Synopsis: Inserts values into the middle of a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: list_set(), list_remove(), list_remove_values()
Usage:
- list = list_insert(list, indices, values);
Description:
Insert values into list before position indices. The indices for insertion
are based on the original list, before any insertions have occurred.
You can use negative indices to count from the end of the list. Note that -1 refers
to the last element, so the insertion will be before the last element.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
list to insert items into |
indices |
index or list of indices where values are inserted |
values |
value or list of values to insert |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = list_insert([3,6,9,12],1,5); // Returns [3,5,6,9,12]
b = list_insert([3,6,9,12],[1,3],[5,11]); // Returns [3,5,6,9,11,12]
Function: list_remove()
Synopsis: Removes items by index from a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: list_set(), list_insert(), list_remove_values()
Usage:
- list = list_remove(list, ind);
Description:
If ind is a number remove list[ind] from the list. If ind is a list of indices
remove from the list the item all items whose indices appear in ind. If you give
indices that are not in the list they are ignored.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to remove items from. |
ind |
index or list of indices of items to remove. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
a = list_remove([3,6,9,12],1); // Returns: [3,9,12]
b = list_remove([3,6,9,12],[1,3]); // Returns: [3,9]
c = list_remove([3,6],3); // Returns: [3,6]
Function: list_remove_values()
Synopsis: Removes items by value from a list.
Topics: List Handling
See Also: list_set(), list_insert(), list_remove()
Usage:
- list = list_remove_values(list, values, [all]);
Description:
Removes the first, or all instances of the given value or list of values from the list.
If you specify all=false and list a value twice then the first two instances will be removed.
Note that if you want to remove a list value such as [3,4] then you must give it as
a singleton list, or it will be interpreted as a list of two scalars to remove.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to modify. |
values |
The value or list of values to remove from the list. |
all |
If true, remove all instances of the value value from the list list. If false, remove only the first. Default: false |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
test = [3,4,[5,6],7,5,[5,6],4,[6,5],7,[4,4]];
a=list_remove_values(test,4); // Returns: [3, [5, 6], 7, 5, [5, 6], 4, [6, 5], 7, [4, 4]]
b=list_remove_values(test,[4,4]); // Returns: [3, [5, 6], 7, 5, [5, 6], [6, 5], 7, [4, 4]]
c=list_remove_values(test,[4,7]); // Returns: [3, [5, 6], 5, [5, 6], 4, [6, 5], 7, [4, 4]]
d=list_remove_values(test,[5,6]); // Returns: [3, 4, [5, 6], 7, [5, 6], 4, [6, 5], 7, [4, 4]]
e=list_remove_values(test,[[5,6]]); // Returns: [3,4,7,5,[5,6],4,[6,5],7,[4,4]]
f=list_remove_values(test,[[5,6]],all=true); // Returns: [3,4,7,5,4,[6,5],7,[4,4]]
animals = ["bat", "cat", "rat", "dog", "bat", "rat"];
animals2 = list_remove_values(animals, "rat"); // Returns: ["bat","cat","dog","bat","rat"]
nonflying = list_remove_values(animals, "bat", all=true); // Returns: ["cat","rat","dog","rat"]
animals3 = list_remove_values(animals, ["bat","rat"]); // Returns: ["cat","dog","bat","rat"]
domestic = list_remove_values(animals, ["bat","rat"], all=true); // Returns: ["cat","dog"]
animals4 = list_remove_values(animals, ["tucan","rat"], all=true); // Returns: ["bat","cat","dog","bat"]
Section: List Iteration Index Helper
Function: idx()
Synopsis: Returns a range useful for iterating over a list.
Topics: List Handling, Iteration
See Also: count()
Usage:
- range = idx(list, [s=], [e=], [step=]);
- for(i=idx(list, [s=], [e=], [step=])) ...
Description:
Returns the range that gives the indices for a given list. This makes is a little bit easier to loop over a list by index, when you need the index numbers and looping of list values isn't enough. Note that the return is a range not a list.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to returns the index range of. |
| By Name | What it does |
|---|---|
s |
The starting index. Default: 0 |
e |
The delta from the end of the list. Default: -1 (end of list) |
step |
The step size to stride through the list. Default: 1 |
Example 1:
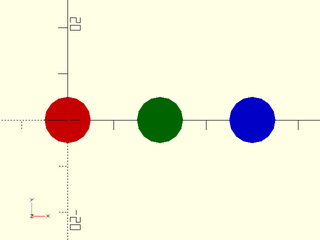
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
colors = ["red", "green", "blue"];
for (i=idx(colors)) right(20*i) color(colors[i]) circle(d=10);
Section: Lists of Subsets
Function: pair()
Synopsis: Returns a list of overlapping consecutive pairs in a list.
Topics: List Handling, Iteration
See Also: idx(), triplet(), combinations(), permutations()
Usage:
- p = pair(list, [wrap]);
- for (p = pair(list, [wrap])) ... // On each iteration, p contains a list of two adjacent items.
Description:
Returns a list of all of the pairs of adjacent items from a list, optionally wrapping back to the front. The pairs overlap, and are returned in order starting with the first two entries in the list. If the list has less than two elements, the empty list is returned.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
The list to use for making pairs |
wrap |
If true, wrap back to the start from the end. ie: return the last and first items as the last pair. Default: false |
Example 1: Does NOT wrap from end to start,
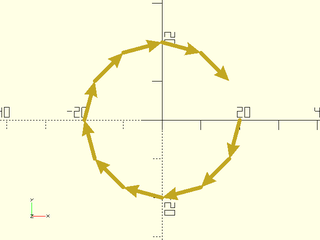
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
for (p = pair(circle(d=40, $fn=12)))
stroke(p, endcap2="arrow2");
Example 2: Wraps around from end to start.
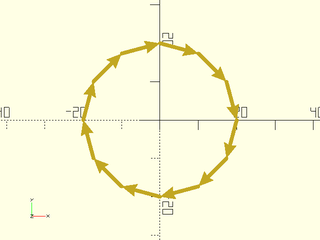
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
for (p = pair(circle(d=40, $fn=12), wrap=true))
stroke(p, endcap2="arrow2");
Example 3:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l = ["A","B","C","D"];
echo([for (p=pair(l)) str(p.y,p.x)]); // Outputs: ["BA", "CB", "DC"]
Function: triplet()
Synopsis: Returns a list of overlapping consecutive triplets in a list.
Topics: List Handling, Iteration
See Also: idx(), pair(), combinations(), permutations()
Usage:
- list = triplet(list, [wrap]);
- for (t = triplet(list, [wrap])) ...
Description:
Returns a list of all adjacent triplets from a list, optionally wrapping back to the front.
If you set wrap to true then the first triplet is the one centered on the first list element, so it includes
the last element and the first two elements. If the list has fewer than three elements then the empty list is returned.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
list |
list to produce triplets from |
wrap |
if true, wrap triplets around the list. Default: false |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
list = [0,1,2,3,4];
a = triplet(list); // Returns [[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[2,3,4]]
b = triplet(list,wrap=true); // Returns [[4,0,1],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[2,3,4],[3,4,0]]
letters = ["A","B","C","D","E"];
[for (p=triplet(letters)) str(p.z,p.y,p.x)]; // Returns: ["CBA", "DCB", "EDC"]
Example 2:
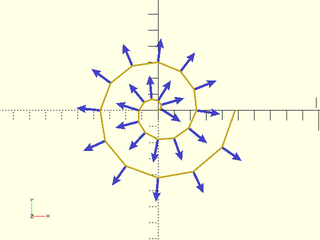
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
path = [for (i=[0:24]) polar_to_xy(i*2, i*360/12)];
for (t = triplet(path)) {
a = t[0]; b = t[1]; c = t[2];
v = unit(unit(a-b) + unit(c-b));
translate(b) rot(from=FWD,to=v) anchor_arrow2d();
}
stroke(path);
Function: combinations()
Synopsis: Returns a list of all combinations of the list entries.
Topics: List Handling, Iteration
See Also: idx(), pair(), triplet(), permutations()
Usage:
- list = combinations(l, [n]);
Description:
Returns a list of all of the (unordered) combinations of n items out of the given list l.
For the list [1,2,3,4], with n=2, this will return [[1,2], [1,3], [1,4], [2,3], [2,4], [3,4]].
For the list [1,2,3,4], with n=3, this will return [[1,2,3], [1,2,4], [1,3,4], [2,3,4]].
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
The list to provide permutations for. |
n |
The number of items in each combination. Default: 2 |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
pairs = combinations([3,4,5,6]); // Returns: [[3,4],[3,5],[3,6],[4,5],[4,6],[5,6]]
triplets = combinations([3,4,5,6],n=3); // Returns: [[3,4,5],[3,4,6],[3,5,6],[4,5,6]]
Example 2:
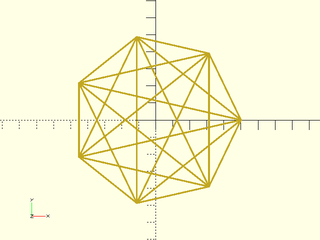
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
for (p=combinations(regular_ngon(n=7,d=100))) stroke(p);
Function: permutations()
Synopsis: Returns a list of all permutations of the list entries.
Topics: List Handling, Iteration
See Also: idx(), pair(), triplet(), combinations()
Usage:
- list = permutations(l, [n]);
Description:
Returns a list of all of the (ordered) permutation n items out of the given list l.
For the list [1,2,3], with n=2, this will return [[1,2],[1,3],[2,1],[2,3],[3,1],[3,2]]
For the list [1,2,3], with n=3, this will return [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
The list to provide permutations for. |
n |
The number of items in each permutation. Default: 2 |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
pairs = permutations([3,4,5,6]); // // Returns: [[3,4],[3,5],[3,6],[4,3],[4,5],[4,6],[5,3],[5,4],[5,6],[6,3],[6,4],[6,5]]
Section: Changing List Structure
Function: list_to_matrix()
Synopsis: Groups items in a list into sublists.
Topics: Matrices, List Handling
See Also: column(), submatrix(), hstack(), flatten(), full_flatten()
Usage:
- groups = list_to_matrix(v, cnt, [dflt]);
Description:
Takes a flat list of values, and groups items in sets of cnt length.
The opposite of this is flatten().
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
v |
The list of items to group. |
cnt |
The number of items to put in each grouping. |
dflt |
The default value to fill in with if the list is not a multiple of cnt items long. Default: undef |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
v = [1,2,3,4,5,6];
a = list_to_matrix(v,2) // returns [[1,2], [3,4], [5,6]]
b = list_to_matrix(v,3) // returns [[1,2,3], [4,5,6]]
c = list_to_matrix(v,4,0) // returns [[1,2,3,4], [5,6,0,0]]
Function: flatten()
Synopsis: Flattens a list of sublists into a single list.
Topics: Matrices, List Handling
See Also: column(), submatrix(), hstack(), full_flatten()
Usage:
- list = flatten(l);
Description:
Takes a list of lists and flattens it by one level.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
List to flatten. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l = flatten([[1,2,3], [4,5,[6,7,8]]]); // returns [1,2,3,4,5,[6,7,8]]
Function: full_flatten()
Synopsis: Recursively flattens nested sublists into a single list of non-list values.
Topics: Matrices, List Handling
See Also: column(), submatrix(), hstack(), flatten()
Usage:
- list = full_flatten(l);
Description:
Collects in a list all elements recursively found in any level of the given list. The output list is ordered in depth first order.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
l |
List to flatten. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
l = full_flatten([[1,2,3], [4,5,[6,7,8]]]); // returns [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
Section: Set Manipulation
Function: set_union()
Synopsis: Merges two lists, returning a list of unique items.
Topics: Set Handling, List Handling
See Also: set_difference(), set_intersection()
Usage:
- s = set_union(a, b, [get_indices]);
Description:
Given two sets (lists with unique items), returns the set of unique items that are in either a or b.
If get_indices is true, a list of indices into the new union set are returned for each item in b,
in addition to returning the new union set. In this case, a 2-item list is returned, [INDICES, NEWSET],
where INDICES is the list of indices for items in b, and NEWSET is the new union set.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
a |
One of the two sets to merge. |
b |
The other of the two sets to merge. |
get_indices |
If true, indices into the new union set are also returned for each item in b. Returns [INDICES, NEWSET]. Default: false |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
set_a = [2,3,5,7,11];
set_b = [1,2,3,5,8];
set_u = set_union(set_a, set_b);
// set_u now equals [2,3,5,7,11,1,8]
set_v = set_union(set_a, set_b, get_indices=true);
// set_v now equals [[5,0,1,2,6], [2,3,5,7,11,1,8]]
Function: set_difference()
Synopsis: Returns a list of unique items that are in list A, but not in list B.
Topics: Set Handling, List Handling
See Also: set_union(), set_intersection()
Usage:
- s = set_difference(a, b);
Description:
Given two sets (lists with unique items), returns the set of items that are in a, but not b.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
a |
The starting set. |
b |
The set of items to remove from set a. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
set_a = [2,3,5,7,11];
set_b = [1,2,3,5,8];
set_d = set_difference(set_a, set_b);
// set_d now equals [7,11]
Function: set_intersection()
Synopsis: Returns a list of unique items that are in both given lists.
Topics: Set Handling, List Handling
See Also: set_union(), set_difference()
Usage:
- s = set_intersection(a, b);
Description:
Given two sets (lists with unique items), returns the set of items that are in both sets.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
a |
The starting set. |
b |
The set of items to intersect with set a. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
set_a = [2,3,5,7,11];
set_b = [1,2,3,5,8];
set_i = set_intersection(set_a, set_b);
// set_i now equals [2,3,5]
Indices
Table of Contents
Function Index
Topics Index
Cheat Sheet
Tutorials
List of Files:
Basic Modeling:
- constants.scad STD
- transforms.scad STD
- attachments.scad STD
- shapes2d.scad STD
- shapes3d.scad STD
- drawing.scad STD
- masks2d.scad STD
- masks3d.scad STD
- distributors.scad STD
- color.scad STD
- partitions.scad STD
- miscellaneous.scad STD
Advanced Modeling:
- paths.scad STD
- regions.scad STD
- skin.scad STD
- vnf.scad STD
- beziers.scad
- nurbs.scad
- rounding.scad
- turtle3d.scad
Math:
- math.scad STD
- linalg.scad STD
- vectors.scad STD
- coords.scad STD
- geometry.scad STD
- trigonometry.scad STD
Data Management:
- version.scad STD
- comparisons.scad STD
- lists.scad STD
- utility.scad STD
- strings.scad STD
- structs.scad STD
- fnliterals.scad
Threaded Parts:
Parts:
- ball_bearings.scad
- cubetruss.scad
- gears.scad
- hinges.scad
- joiners.scad
- linear_bearings.scad
- modular_hose.scad
- nema_steppers.scad
- polyhedra.scad
- sliders.scad
- tripod_mounts.scad
- walls.scad
- wiring.scad
Footnotes:
STD = Included in std.scad