Table of Contents
- LibFile: trigonometry.scad
- File Contents
- Section: 2D General Triangle Functions
- Section: 2D Right Triangle Functions
- Function: hyp_opp_to_adj()
- Function: hyp_ang_to_adj()
- Function: opp_ang_to_adj()
- Function: hyp_adj_to_opp()
- Function: hyp_ang_to_opp()
- Function: adj_ang_to_opp()
- Function: adj_opp_to_hyp()
- Function: adj_ang_to_hyp()
- Function: opp_ang_to_hyp()
- Function: hyp_adj_to_ang()
- Function: hyp_opp_to_ang()
- Function: adj_opp_to_ang()
This file contains Unicode characters that might be confused with other characters. If you think that this is intentional, you can safely ignore this warning. Use the Escape button to reveal them.
LibFile: trigonometry.scad
Trigonometry shortcuts for people who can't be bothered to remember all the function relations, or silly acronyms like SOHCAHTOA.
To use, add the following lines to the beginning of your file:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
File Contents
-
Section: 2D General Triangle Functions
law_of_cosines()– Applies the Law of Cosines for an arbitrary triangle.law_of_sines()– Applies the Law of Sines for an arbitrary triangle.
-
Section: 2D Right Triangle Functions
hyp_opp_to_adj()– Returns the adjacent side length from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the opposite side.hyp_ang_to_adj()– Returns the adjacent side length from the length of the hypotenuse and the angle.opp_ang_to_adj()– Returns the adjacent side length from the length of the opposite side and the angle.hyp_adj_to_opp()– Returns the opposite side length from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side.hyp_ang_to_opp()– Returns the opposite side length from the length of the hypotenuse and the angle.adj_ang_to_opp()– Returns the opposite side length from the length of the adjacent side and the angle.adj_opp_to_hyp()– Returns the hypotenuse length from the lengths of the adjacent and opposite sides.adj_ang_to_hyp()– Returns the hypotenuse length from the length of the adjacent and the angle.opp_ang_to_hyp()– Returns the hypotenuse length from the length of the opposite side and the angle.hyp_adj_to_ang()– Returns the angle from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side.hyp_opp_to_ang()– Returns the angle from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the opposite side.adj_opp_to_ang()– Returns the angle from the lengths of the adjacent and opposite sides.
Section: 2D General Triangle Functions
Function: law_of_cosines()
Synopsis: Applies the Law of Cosines for an arbitrary triangle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: law_of_sines()
Usage:
- C = law_of_cosines(a, b, c);
- c = law_of_cosines(a, b, C=);
Description:
Applies the Law of Cosines for an arbitrary triangle. Given three side lengths, returns the angle in degrees for the corner opposite of the third side. Given two side lengths, and the angle between them, returns the length of the third side.
Figure 1.1.1:
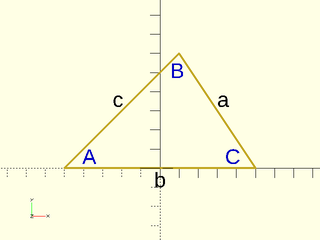
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
a |
The length of the first side. |
b |
The length of the second side. |
c |
The length of the third side. |
| By Name | What it does |
|---|---|
C |
The angle in degrees of the corner opposite of the third side. |
Function: law_of_sines()
Synopsis: Applies the Law of Sines for an arbitrary triangle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: law_of_cosines()
Usage:
- B = law_of_sines(a, A, b);
- b = law_of_sines(a, A, B=);
Description:
Applies the Law of Sines for an arbitrary triangle. Given two triangle side lengths and the angle between them, returns the angle of the corner opposite of the second side. Given a side length, the opposing angle, and a second angle, returns the length of the side opposite of the second angle.
Figure 1.2.1:
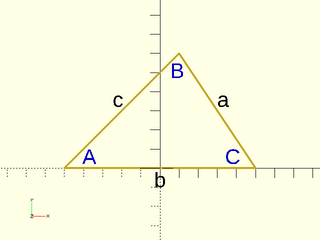
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
a |
The length of the first side. |
A |
The angle in degrees of the corner opposite of the first side. |
b |
The length of the second side. |
| By Name | What it does |
|---|---|
B |
The angle in degrees of the corner opposite of the second side. |
Section: 2D Right Triangle Functions
This is a set of functions to make it easier to perform trig calculations on right triangles. In general, all these functions are named using these abbreviations:
- hyp: The length of the Hypotenuse.
- adj: The length of the side adjacent to the angle.
- opp: The length of the side opposite to the angle.
- ang: The angle size in degrees.
If you know two of those, and want to know the value of a third, you will need to call a
function named like AAA_BBB_to_CCC(). For example, if you know the length of the hypotenuse,
and the length of the side adjacent to the angle, and want to learn the length of the side
opposite to the angle, you will call opp = hyp_adj_to_opp(hyp,adj);.
Figure 2.1:
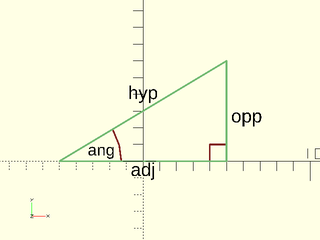
Function: hyp_opp_to_adj()
Alias: opp_hyp_to_adj()
Synopsis: Returns the adjacent side length from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the opposite side.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- adj = hyp_opp_to_adj(hyp,opp);
- adj = opp_hyp_to_adj(opp,hyp);
Description:
Given the lengths of the hypotenuse and opposite side of a right triangle, returns the length of the adjacent side.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
hyp |
The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. |
opp |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is opposite from the primary angle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
hyp = hyp_opp_to_adj(5,3); // Returns: 4
Function: hyp_ang_to_adj()
Alias: ang_hyp_to_adj()
Synopsis: Returns the adjacent side length from the length of the hypotenuse and the angle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- adj = hyp_ang_to_adj(hyp,ang);
- adj = ang_hyp_to_adj(ang,hyp);
Description:
Given the length of the hypotenuse and the angle of the primary corner of a right triangle, returns the length of the adjacent side.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
hyp |
The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. |
ang |
The angle in degrees of the primary corner of the right triangle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
adj = hyp_ang_to_adj(8,60); // Returns: 4
Function: opp_ang_to_adj()
Alias: ang_opp_to_adj()
Synopsis: Returns the adjacent side length from the length of the opposite side and the angle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- adj = opp_ang_to_adj(opp,ang);
- adj = ang_opp_to_adj(ang,opp);
Description:
Given the angle of the primary corner of a right triangle, and the length of the side opposite of it, returns the length of the adjacent side.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
opp |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is opposite from the primary angle. |
ang |
The angle in degrees of the primary corner of the right triangle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
adj = opp_ang_to_adj(8,30); // Returns: 4
Function: hyp_adj_to_opp()
Alias: adj_hyp_to_opp()
Synopsis: Returns the opposite side length from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- opp = hyp_adj_to_opp(hyp,adj);
- opp = adj_hyp_to_opp(adj,hyp);
Description:
Given the length of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side, returns the length of the opposite side.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
hyp |
The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. |
adj |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is adjacent to the primary angle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
opp = hyp_adj_to_opp(5,4); // Returns: 3
Function: hyp_ang_to_opp()
Alias: ang_hyp_to_opp()
Synopsis: Returns the opposite side length from the length of the hypotenuse and the angle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- opp = hyp_ang_to_opp(hyp,ang);
- opp = ang_hyp_to_opp(ang,hyp);
Description:
Given the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, and the angle of the corner, returns the length of the opposite side.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
hyp |
The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. |
ang |
The angle in degrees of the primary corner of the right triangle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
opp = hyp_ang_to_opp(8,30); // Returns: 4
Function: adj_ang_to_opp()
Alias: ang_adj_to_opp()
Synopsis: Returns the opposite side length from the length of the adjacent side and the angle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- opp = adj_ang_to_opp(adj,ang);
- opp = ang_adj_to_opp(ang,adj);
Description:
Given the length of the adjacent side of a right triangle, and the angle of the corner, returns the length of the opposite side.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
adj |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is adjacent to the primary angle. |
ang |
The angle in degrees of the primary corner of the right triangle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
opp = adj_ang_to_opp(8,45); // Returns: 8
Function: adj_opp_to_hyp()
Alias: opp_adj_to_hyp()
Synopsis: Returns the hypotenuse length from the lengths of the adjacent and opposite sides.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- hyp = adj_opp_to_hyp(adj,opp);
- hyp = opp_adj_to_hyp(opp,adj);
Description:
Given the length of the adjacent and opposite sides of a right triangle, returns the length of the hypotenuse.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
adj |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is adjacent to the primary angle. |
opp |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is opposite from the primary angle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
hyp = adj_opp_to_hyp(3,4); // Returns: 5
Function: adj_ang_to_hyp()
Alias: ang_adj_to_hyp()
Synopsis: Returns the hypotenuse length from the length of the adjacent and the angle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- hyp = adj_ang_to_hyp(adj,ang);
- hyp = ang_adj_to_hyp(ang,adj);
Description:
For a right triangle, given the length of the adjacent side, and the corner angle, returns the length of the hypotenuse.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
adj |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is adjacent to the primary angle. |
ang |
The angle in degrees of the primary corner of the right triangle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
hyp = adj_ang_to_hyp(4,60); // Returns: 8
Function: opp_ang_to_hyp()
Alias: ang_opp_to_hyp()
Synopsis: Returns the hypotenuse length from the length of the opposite side and the angle.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj()
Usage:
- hyp = opp_ang_to_hyp(opp,ang);
- hyp = ang_opp_to_hyp(ang,opp);
Description:
For a right triangle, given the length of the opposite side, and the corner angle, returns the length of the hypotenuse.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
opp |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is opposite from the primary angle. |
ang |
The angle in degrees of the primary corner of the right triangle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
hyp = opp_ang_to_hyp(4,30); // Returns: 8
Function: hyp_adj_to_ang()
Alias: adj_hyp_to_ang()
Synopsis: Returns the angle from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent side.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- ang = hyp_adj_to_ang(hyp,adj);
- ang = adj_hyp_to_ang(adj,hyp);
Description:
For a right triangle, given the lengths of the hypotenuse and the adjacent sides, returns the angle of the corner.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
hyp |
The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. |
adj |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is adjacent to the primary angle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
ang = hyp_adj_to_ang(8,4); // Returns: 60 degrees
Function: hyp_opp_to_ang()
Alias: opp_hyp_to_ang()
Synopsis: Returns the angle from the lengths of the hypotenuse and the opposite side.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_ang(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- ang = hyp_opp_to_ang(hyp,opp);
- ang = opp_hyp_to_ang(opp,hyp);
Description:
For a right triangle, given the lengths of the hypotenuse and the opposite sides, returns the angle of the corner.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
hyp |
The length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. |
opp |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is opposite from the primary angle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
ang = hyp_opp_to_ang(8,4); // Returns: 30 degrees
Function: adj_opp_to_ang()
Alias: opp_adj_to_ang()
Synopsis: Returns the angle from the lengths of the adjacent and opposite sides.
Topics: Geometry, Trigonometry, Triangles
See Also: adj_ang_to_hyp(), adj_ang_to_opp(), adj_opp_to_hyp(), hyp_adj_to_ang(), hyp_adj_to_opp(), hyp_ang_to_adj(), hyp_ang_to_opp(), hyp_opp_to_adj(), hyp_opp_to_ang(), opp_ang_to_adj(), opp_ang_to_hyp()
Usage:
- ang = adj_opp_to_ang(adj,opp);
- ang = opp_adj_to_ang(opp,adj);
Description:
For a right triangle, given the lengths of the adjacent and opposite sides, returns the angle of the corner.
Arguments:
| By Position | What it does |
|---|---|
adj |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is adjacent to the primary angle. |
opp |
The length of the side of the right triangle that is opposite from the primary angle. |
Example 1:
include <BOSL2/std.scad>
ang = adj_opp_to_ang(sqrt(3)/2,0.5); // Returns: 30 degrees
Indices
Table of Contents
Function Index
Topics Index
Cheat Sheet
Tutorials
List of Files:
Basic Modeling:
- constants.scad STD
- transforms.scad STD
- attachments.scad STD
- shapes2d.scad STD
- shapes3d.scad STD
- drawing.scad STD
- masks2d.scad STD
- masks3d.scad STD
- distributors.scad STD
- color.scad STD
- partitions.scad STD
- miscellaneous.scad STD
Advanced Modeling:
- paths.scad STD
- regions.scad STD
- skin.scad STD
- vnf.scad STD
- beziers.scad
- nurbs.scad
- rounding.scad
- turtle3d.scad
Math:
- math.scad STD
- linalg.scad STD
- vectors.scad STD
- coords.scad STD
- geometry.scad STD
- trigonometry.scad STD
Data Management:
- version.scad STD
- comparisons.scad STD
- lists.scad STD
- utility.scad STD
- strings.scad STD
- structs.scad STD
- fnliterals.scad
Threaded Parts:
Parts:
- ball_bearings.scad
- cubetruss.scad
- gears.scad
- hinges.scad
- joiners.scad
- linear_bearings.scad
- modular_hose.scad
- nema_steppers.scad
- polyhedra.scad
- sliders.scad
- tripod_mounts.scad
- walls.scad
- wiring.scad
Footnotes:
STD = Included in std.scad